The basement can account for 20 to 30 percent of the total heat loss of a home. This is because of the large, uninsulated surface area both above and below grade level. By adding insulation and sealing air leaks with caulking, weather stripping and an effective air vapour retarder, heat loss can be reduced to create a more comfortable home.
PREPARING TO INSULATE
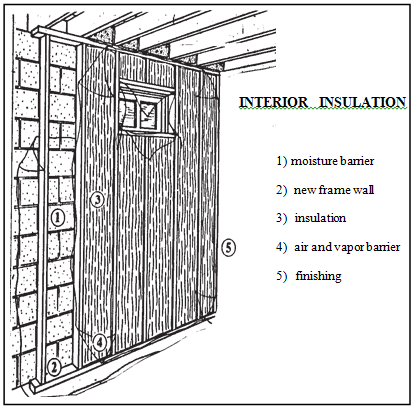
The most critical consideration when insulating a basement is moisture, both internally and externally generated. Moisture can ruin insulation and rot wood. Uncorrected moisture problems can also cause serious structural damage.
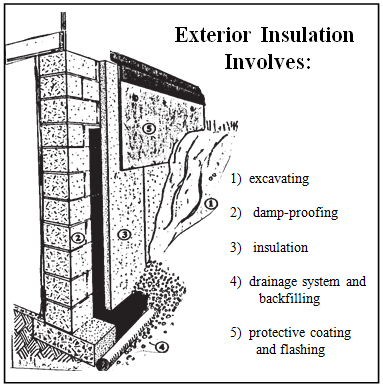
The first step is to ensure that the surface drainage is adequate. Eavestroughs, drains and pavement should be properly sloped to take the water away from the house. Basements often have high humidity, caused by dampness in the foundation walls. Dehumidifiers can decrease the humidity level if the problem is minor. Once the moisture problem has been eliminated, the basement can be insulated either from the inside or the outside. In most cases, insulating from the outside is best, though often it is necessary to insulate from the inside for economical and practical reasons. Sometimes a combination of both is required.
WHAT IS AN R OR RSI VALUE?
An R-value is simply a numerical representation of thermal resistance. The higher the number, the greater the resistance to heat transfer. RSI values are the metric equivalent of R-values. Different types of insulation have different R-values per inch of thickness. Even the same type of insulation can have a different R-value depending on its form. Glass fiber insulation has a higher R-value in batt form than in the loose fill form.
There are many different types of insulation on the market today. The following chart identifies types and R-values of the most common.
| Material | R-Value/Inch | Common Form |
| Glass Fiber | 2.0 – 4.2 | batt, loose fill, rigid |
| Mineral Wool | 3.0 – 3.2 | batt, loose fill |
| Cellulose Fiber | 3.4 – 3.6 | loose fill |
| Vermiculite | 2.3 | loose fill |
| Plastic Board | 3.7 – 6.0 | rigid board |